Case
|
Enron |
Foundations of Business |
| description | issues | material & sources |
| Energy giant Enron was once the seventh largest company
in the USA, and its collapse in late 2001 was the largest corporate failure
in US history.
Shareholders Enron chairman and chief executive Ken Lay pocketed millions of dollars by offloading shares over the past few years. Meanwhile, many employees of Enron lost the bulk of their
life savings and pension, which were tied up in Enron shares.
Political connections Enron was a generous donor to US politicians, funding both Republicans and Democrats. Ken Lay had close ties to President George W. Bush, both before and after his election. Enron was also the leading corporate donor to the re-election
campaigns of Texas Supreme Court judges between 1993 and 2001. At this
time, Enron was a party to six petitions for review before the court.
Concealed debt Enron used special-purpose vehicles (including one named Jedi II) to hide debt from shareholders. |
Economics What was the Enron business model, was
it economically viable? What is the role of accountancy and audit in this
case?
Compare and contrast the new "asset-light" economy with
the old "asset-heavy" economy in ethical terms. What are the likely differences
in system behaviour?
Ethics Who were the stakeholders? How were their interests represented? Why do you think Enron had an ethical code? Why do you
think it was so easy for Enron directors to bypass the code?
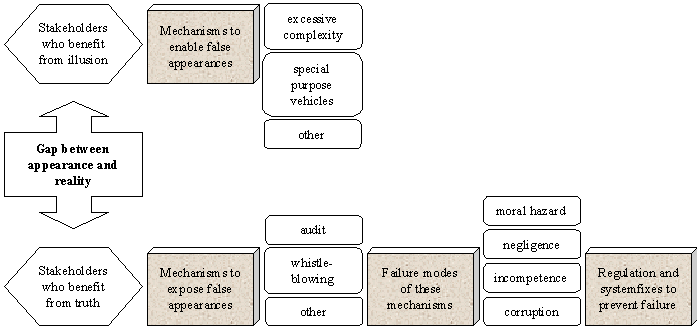
Systems Theory Discuss the gap between public illusion (including financial accounts) and private reality. What enabled the construction of this illusion? What mechanisms were supposed to puncture such illusion, and how did these mechanisms fail? Social What new mechanisms and fixes, relationships and regulations are proposed to prevent future Enrons? How effective are these likely to be? |
Recommended Book: John Plender, Going off the
Rails. John Wiley, 2003.
www.Laydoff.com - a website established by former Enron employees www.ft.com/enron - Financial Times |
October 2001. Enron eliminates $1.2bn of shareholder equity. Enron stock falls from $90 per share to practically nothing.
October 31, 2001. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) announce a formal investigation into the finances of Enron.
November 21, 2001. Shareholder lawsuit filed by Amalgamated Bank and the AFL-CIO.
January 15th, 2002. It is revealed that Enron’s auditor, Andersen, had shredded and deleted documents relating to Enron after receiving subpoenas from regulators.
January 22nd, 2002. It is alleged that Enron itself had also shredded and deleted documents
 |
 |
| [top] |
Copyright © 2002-4 Veryard Projects Ltd & Antelope Projects Ltd http://www.veryard.com/orgmgt/caseenron.htm |