  |
software componentry |
| software componentry | on this page | materials & resources | internet links | home |
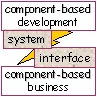
| cbb = component-based
business
cbd = component-based development cbse = component-based software engineering odp = open distributed processing
Trends |
veryard projects
typical services veryard projects
papers on CBD we recommend
CBD books |
please read
component
ecosystems the context for software componentry
web services
|

Cetus Links
|
|
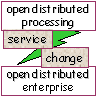
cbb cbd cbse odp
|
||

 |
component (always
software? same as Object?)
encapsulation interface plug'n'play reuse specification |
What
is CBD?
|
 |
Trendsveryard projects > cbse > trends |
| Growth of web services. The advent of web services represents an important stage in the transition of software into tradeable commodities. Software componentry involves a separation of the external services (the "commodity" that provides value to the consumer) from the internal mechanism. Web services takes this separation one step further - so that the mechanism itself is hidden, and the consumer pays for the services rather than the mechanism. | |
| Growth of telecoms. While the software industry follows the drama being played out by IBM, Microsoft, Oracle and Sun, the telecoms companies are quietly staking out an important position. | |
| Growth of biological metaphors. Software components (including so-called intelligent agents) are released into a giant (global) ecosystem. Some move about and reproduce themselves (like animals). Some remain stationary and disseminate copies and links to themselves (like plants). | |
| Extending 'plug-and-play' into the business arena. Constructing solutions from ready-made building blocks (plug-and-play) seems very attractive, not just for software, but for whole business operations. | |
| Convergence of engineering and economics. Proper system of metrics - linking engineering characteristics with ecological success and commercial value. Option pricing and the hedonic pricing model may be applied to software components. |
 |
Myths of Component-Based Software Engineeringveryard projects > cbse > myths |
| The primary task of CBSE is to build software components. | Wrong. The whole point is NOT to build components. Not-Building leads to Not-Testing, Not-Maintaining, Not-Monkeying-Around. | |
| Trust and security can be achieved by installing trustworthy components. | Wrong. Trust and security are system-wide properties, and are not localized in a single component. | |
| A software component satisfies a unique specification. | Wrong. If a component satisfies a given specification, it also satisfies all weaker specifications. | |
 |
Typical Servicesveryard projects > cbse > services |
| Introduction | We can introduce CBD into your software process.
We can focus your software process on achieving software economies of scale. |
| Investigation | We can investigate CBD opportunities for your business processes or
software provision.
We can identify and evaluate your options within the software supply chain. |
| Assessment | We can assess your plans, projects, systems and organizations from a CBD perspective. |
| Education & training | We can provide training in CBD and related topics. |
| Execution | We can provide planning, analysis, design, testing and other development services. |
We are happy to work with a variety of CBD methods.
Our preference is for the SCIPIO
method.
Please contact us to discuss further.
![]()
 |
White Papers and Other Materialsveryard projects > cbse > materials |
|
|
|
|
| Component Design (HTML) | connectivity, flexibility, availability, quality, economies of scale, pleasure | May 1999 |
| Component Ecosystems (HTML)
The context for CBD |
components, encapsulation, reuse, plug'n'play | April 1999 |
| Component Requirements (HTML)
Understanding Business Requirements in terms of Components (Acrobat file) Defining Requirements for Software Components (Acrobat file) |
requirements | April 1999 |
| Software Component Quality (HTML) | quality, testing | February 1997 |
| Component-Based Development for Y2K and Euro(HTML) | CBD, Year 2000, Euro | January 1999 |
| CBD and ODP Briefing (Acrobat file) | January 1999 | |
![]()
 |
Books on Software Componentsveryard projects > cbse > books |
 |
| title |
|
|
| John Cheesman & John Daniels
UML Components
Addison Wesley, 2000 |
 |
 |
| Desmond D'Souza & Alan Cameron Wills
Objects, Components and Frameworks with UML:
Addison-Wesley, 1999 |
 |
 |
| Paul Allen & Stuart Frost
Component-Based Development for Enterprise Systems:
Cambridge University Press & SIGS Books, 1998 |
 |
 |
| Richard Veryard
Component-Based Business: Plug and Play Springer 2001 |
now available | now available |
| Books on Patterns | |
| Object
Oriented Books
electronic commerce, intelligent agent Object-Oriented Technology, BPR, HCI, OO Methods. OO Prog |
| top |  |
|
|
Copyright © 1997-2001 Veryard Projects Ltd http://www.veryard.com/CBDmain/index.htm |