

Zeiss bridge micoscope |
H&E |
CR-39 alpha-image |
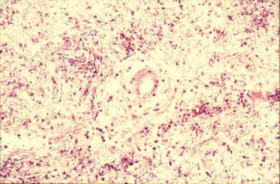
H&E |
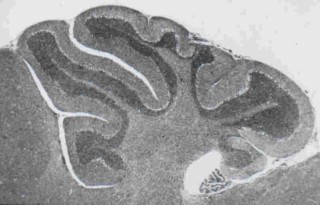
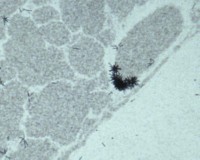
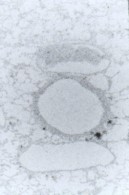
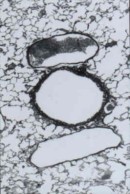
Brain |
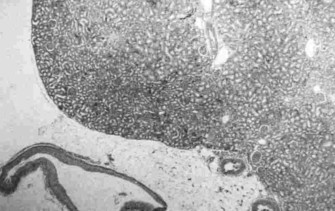
Kidney |
Boronated tissue n-alpha images |
Cytospin |
Phase contrast |
H&E |
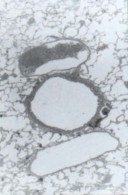
SEM electron probe elemental analysis |
SEM |
Above: Lavaged alveolar macrophages recovered from the lung after the inhalation
of fibres |
H&E |
Return to Home Page |
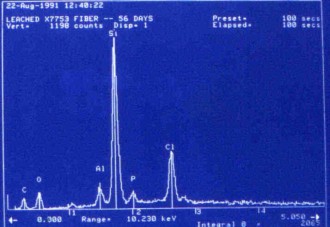
An SEM photomicrograph of glass fibres prior to inhalation |
Elemental analysis of these fibres after 56 days in the lung |
Images of brain and kidney tissue made in CR-39 plastic slides using the boron-10
n,alpha reaction |
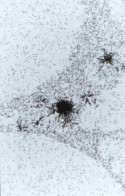
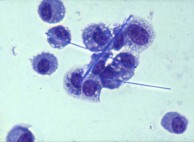
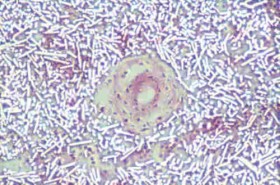
Particles of uranium dioxide in the process of being cleared from the lungs by alveolar
macrophages |
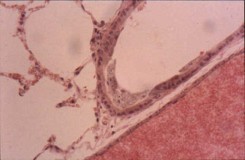
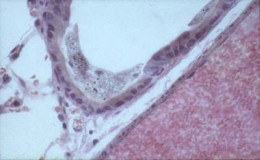
The visualisation of glass fibres on intra-peritoneal tissue using phase contrast
optical microscopy |
The use of Boron -10 and various atomic reactor neutron fluences to produce images
of lung tissue and inhaled uranium-235 fission fragment tracks without destroying
the original tissue section (seen right in b&w) |
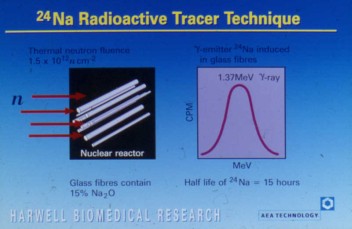
Above: A radioactive in vivo tracer technique for measuring the dose and initial clearance of inhaled glass fibres
using the isotope sodium-24 |
Gallery |
The FACStar Flow Cytometer |

The Biomedical Research high resolution gamma scintillation counter |

Another manual gamma scintillation counter with heavy lead shielding |

Fused aluminosilicate clay particle (FAP) production for lung distribution studies |

Biomedical's histology laboratory |
Return to the Magiscan Page |
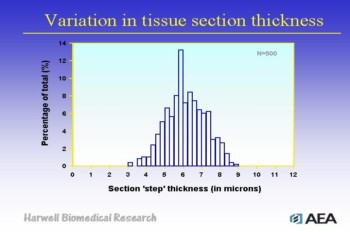
Above: Investigating the variation in the thickness of resin embedded histological
sections cut to a nominal thickness of 5Ám (n=500) |
High mag |